PyGameの迷路のコントローラーとしてM5stackを使ってみた。
M5stackとMacとの通信は以下の方法で。
https://isehara-3lv.sakura.ne.jp/blog/2022/05/05/m5stack-bluetoothでのmacとの送受信/
迷路ゲームについては、迷路作成は壁のばし法
のクラスファイル流用して、ゲーム本体は、
https://news.mynavi.jp/techplus/article/zeropython-90/
から迷路作成ロジックだけ入れ替えですが、ほぼそのまま使えました。
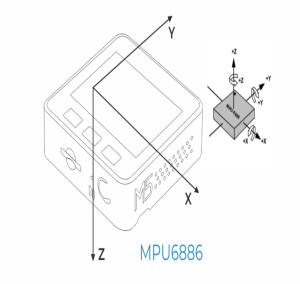
M5stackのボタン処理は、ボタンが三つしか無いから、そのままではL/R/U/Dの処理ができないから、M5stackを傾けてボタンA/Cを操作したらU/Dになるように重力加速度の値で読み替えしてます。
ゲーム中にボタンBを押すとゲーム終了します。
#define M5STACK_MPU6886
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
#include <M5Stack.h>
BluetoothSerial bts;
String btn;
float accX = 0.0F; // Define variables for storing inertial sensor data
float accY = 0.0F;
float accZ = 0.0F;
float angle_th = 0.5F; // r/l or u/l decision threashold
void read_imu() {
M5.IMU.getAccelData(&accX,&accY,&accZ); //Stores the triaxial accelerometer.
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 90);
M5.Lcd.printf(" accX");
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 130);
M5.Lcd.printf("%5.2f G", accX);
}
void setup() {
M5.begin();
M5.Power.begin(); //Init Power module.
M5.IMU.Init(); //Init IMU sensor.
M5.Lcd.setRotation(3);
M5.Lcd.fillScreen(BLACK);
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 0, 2);
M5.Lcd.println("Maze game");
bts.begin("ESP32test");
}
void loop() {
btn = ""; // button info. clear
M5.update();
if(M5.BtnA.wasPressed())
{
btn = "r";
}
if(M5.BtnB.wasPressed())
{
btn = "t";
}
if(M5.BtnC.wasPressed())
{
btn = "l";
}
read_imu(); // imu data read
if(btn != "")
{
if (btn != "t") // t(ButtonB) key terminate the Maze game
{
if (accX < -angle_th | accX > angle_th) // if M5stack is tilted, r/l keys are changed to u/d
{
if (accX < -angle_th){ if (btn == "r") { btn = "u"; } else { btn = "d"; } } if (accX > angle_th)
{
if (btn == "r")
{
btn = "d";
}
else
{
btn = "u";
}
}
}
}
bts.println(btn); // send pressed key info.
M5.Lcd.setCursor(0, 50, 2);
M5.Lcd.println(btn);
}
delay(100);
}Bluetoothシリアルがコードを弄ってると繋がらなくなることが頻繁に起きて、その都度リブートしてるのは面倒です。本質的な原因はなんなんだろう?
全体のコードは、
https://github.com/chateight/PlatformIO/tree/master/bte_serial/src
にあります。
pythonのmaze.pyがメイン処理、make_maze.pyが迷路作成コード、receive.pyはM5stackのキー入力確認用のスクリプトでゲームと直接は関係ありません。
admin