ラズパイ5のluantiサーバーの管理者とユーザーは少なくとも別のメールアカウントにしないと、サーバー含めた管理者エリアへのアクセスができてしまうので現実運用に即した多少のアップデート
つまり管理者エリアとユーザエリアはメールアカウントを別にして、ユーザアカウントの管理画面には最悪アクセスできても管理者エリアの管理画面へのアクセスは禁止する設定
ユーザデバイスは以下のuser@gmail.com(仮想のアドレスです)の配下に登録、管理者デバイスはadmin@gmail.comの配下に登録します
"groups": {
"group:admin": ["admin@gmail.com"],
"group:players": ["admin@gmail.com", "user@gmail.com"],
},
// Define the tags which can be applied to devices and by which users.
// "tagOwners": {
// "tag:example": ["autogroup:admin"],
// },
"tagOwners": {
"tag:luanti-server": ["group:admin"],
},
// Define grants that govern access for users, groups, autogroups, tags,
// Tailscale IP addresses, and subnet ranges.
"acls": [
{
"action": "accept",
"src": ["group:players"],
"dst": [
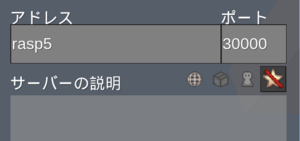
"tag:luanti-server:30000-30010",
"tag:luanti-server:22",
"tag:luanti-server:5900",
"tag:luanti-server:5901",
],
},
],user@gmail.com側のドメインではACL設定はできないので、user@gmail.com側の相互ユーザ分離はできないですが、それは通常のWi-Fi環境下と大差はないだろうから現実的運用では、管理者エリアとユーザエリアを分離だけでも相当にセキュアだろうと思う
P.S. 2026/2/21
"tag:luanti-server:5900",
"tag:luanti-server:5901",
5900 portも通過許容に変更、そうしないとVNCがtailscale経由では通らない
P.S. 2026/2/23
tailscaleの管理者機能で、
tailscaleのアカウント切り替えは、一台のクライアントで登録は一個だけに限定されるからログアウトして再登録する必要がある、VMwareで例えばLinux動かしとけば、実質二台のPCとして使えるから2個のtailscaleアカウントを一台で持つことができる
admin