今時の言語のGoをしばらく触ってみます。とりあえずのゴールはラズパイでWebサーバー構築してM5Stackとやりとりすること。node.jsと同等の機能が実現できるはずで、コンパイラーであるだけ高速でしょう。

とりあえずM1 Macと初代に限りなく近いRaspberry PIにインストールしてみました。
— M1 Mac環境 —
<install>
% brew install go
するだけ、
% go version
go version go1.19.4 darwin/arm64
が今の最新版数のようです。
VScodeはGoマークの拡張機能を二つインストールしただけでソースコード編集ができます、追加で必要ならばインストールを要求されます。
<directory>
ユーザディレクトリ直下にgoという名前で作成されます。
<初めてのソース>
定番ですが、
package main
import "fmt"
func main(){
fmt.Println("hello Go")
}
WordPressのアドオン古くてGo言語選択できないので近そうなC++にしています。
import “fmt”は他言語のimport “sys”のようなものでしょうか。
<module>
そこそこの規模になるとモジュール化が必要ですが、先ほどのソースディレクトリにモジュール用のディレクトリ作成してモジュールを作成します。
% mkdir mod
% cd mod
% go mod init mod
% cp ../hello_go.go ./
% go mod tidy
% go build
% ./mod
hello Go
全体のディレクトリ構成は以下のようになります@VScode
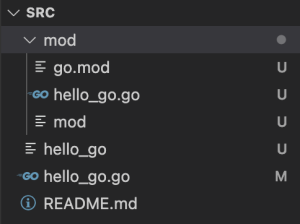
通常の% go runでは実行ファイルはテンポラリに作成され実行後に削除されるようですが、実行ファイルを残すためには% go buildを使います。
このようにgoコマンドのパラメータ指定で作業をコントロールできるようになっています。
— RaspberryPI 環境 —
https://zenn.dev/ysmtegsr/articles/20d6e0c7159be2
を参考にインストール、
$ wget https://go.dev/dl/go1.19.4.linux-armv6l.tar.gz
$ sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.19.4.linux-armv6l.tar.gz
/usr/local/go/bin/に移動して、
$ ./go version
go version go1.19.4 linux/arm
まだパスが通っていない、
パスを通す、
$ echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin' >> ~/.bashrc
$ echo 'export PATH=$HOME/go/bin:$PATH' >> ~/.bashrc
$ source ~/.bashrc
Macと同じような簡単なソースファイル(main.go)をgo_prj配下に作る、
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello world")
}
$ go mod init go_prj
$ cd go_prj
$ tree ../go_prj
../go_prj
├── go.mod
├── main
└── main.go
$ go run
コンパイル実行だとRaspberryPIでは数秒待つから遅い
$ go build -o main
$ ./main
で実行ファイル呼び出すと高速(当然ですが)、この起動時間待ちの雰囲気はnode.jsの起動でも同じだからRaspberry PiではGoをbuildして使うのが普通になると思います。
Go言語の第一印象
随所に現代的(ビルド環境やソースコードの検証など、まだイントロしか読んでいないからこの程度)なところを見ることができます。既存の言語はバージョンアップでも過去との互換を考えないといけないわけですが、新たな言語はその時点で必要な機能を順位づけして言語仕様や開発環境を決めることが出来るわけですから。
admin